pacman::p_load(sf, sfdep, tmap, tidyverse, knitr, plotly)In-class_Ex2: Spatial Weights - sfdep methods
Getting started
Installing and Loading the R Packages
Four R packages will be used for this in-class exercise, theu are sf, sfdep, tmap, tidyverse.
- knitr is to generate HTML table
- tidyverse consists of many different packages
The Data
For the purpose of this in-class exercise, the Hunan data sets will be used. Theree are two data sets in this use case, they are:
- Hunan, a geospatial data set in ESRI sharefile format, and
- Hunan_2012, an attribute data set in csv format
Importing geospatial data
hunan <- st_read(dsn = "data/geospatial",
layer = "Hunan")Reading layer `Hunan' from data source
`C:\chiays\ISS624\In-class_Ex\In-class_Ex2\data\geospatial'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Importing attribute table
hunan_2012 <- read_csv("data/aspatial/Hunan_2012.csv")Rows: 88 Columns: 29
── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Delimiter: ","
chr (2): County, City
dbl (27): avg_wage, deposite, FAI, Gov_Rev, Gov_Exp, GDP, GDPPC, GIO, Loan, ...
ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.Combining both dataframe by using left join
:::
Show the code
hunan_GDPPC <- left_join(hunan, hunan_2012) %>%
select(1:4,7,15)Joining with `by = join_by(County)`- left_join keeps all observations in x
- right_join keeps all observation in y
- inner_join only keeps observations from x that have a matching key in y
::: callout-important In order to retain the geospatial properties, the left dataframe must be the sf data.frame (i.e. hunan)
Plotting a choropleth map
The choropleth should look similar to ther figure below.
tmap_mode("plot")tmap mode set to plottingtm_shape(hunan_GDPPC) +
tm_fill("GDPPC",
style = "quantile",
palette = "Blues",
title = "GDPPC") +
tm_borders(alpha = 0.5) +
tm_layout(main.title = "Distribution of GDP per capita by district, Hunan Province",
main.title.position = "center",
main.title.size = 1.2,
legend.height = 0.45,
legend.width = 0.35,
frame = TRUE) +
tm_compass(type="8star", size = 2) +
tm_scale_bar() +
tm_grid(alpha =0.2)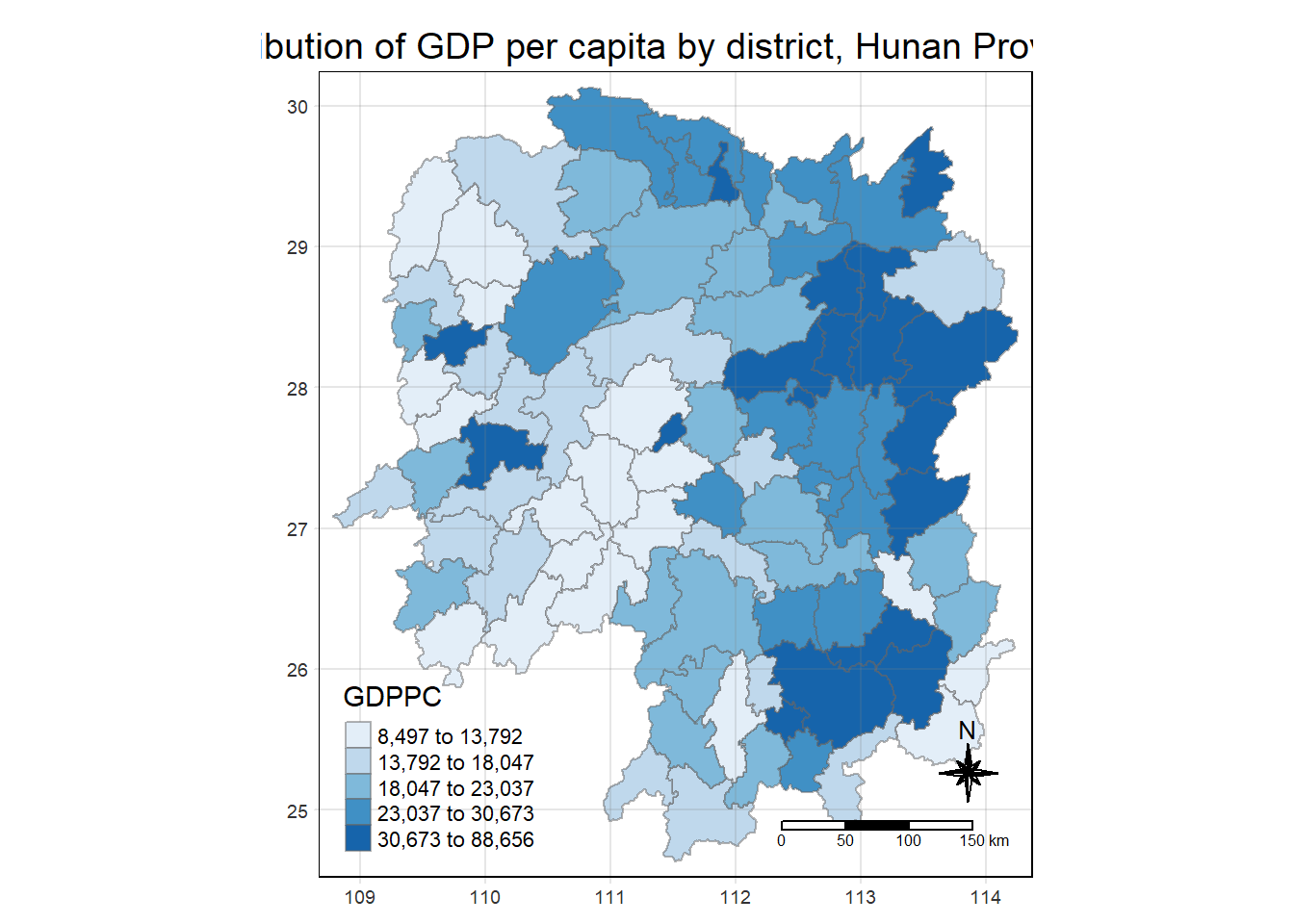
Deriving contiguity Spatial Weights
By and large, there are two types of spatial weights, they are contiguity weights and distance-based weights. In this section, you will learn how to derive contiguity spatial weights by using sfdep.
Two steps are required to derive a contiguity spatial weights, they are:
identifying contiguity neighbour list by st_contiguity() of sfdep package, and
deriving the contiguity spatial weights by using st_weights() of sfdep package
In this section, we will learn how to derive the contiguity neighbour list and contiguity spatial weights separately. Then, we will learn how to combine both steps into a single process.
Identifying contiguity neighbours: Queen’s method
In the code chunk below st_contiguity() is used to derive a contiguity neighbour list by using Queen’s method.
Deriving contiguity weights: Queen’s method
nb_queen <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
.before = 1)The code chunk below is used to print the summary of the first lag neighbour list (i.e. nb).
summary(nb_queen$nb)Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 448
Percentage nonzero weights: 5.785124
Average number of links: 5.090909
Link number distribution:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11
2 2 12 16 24 14 11 4 2 1
2 least connected regions:
30 65 with 1 link
1 most connected region:
85 with 11 linksThe summary report above shows that there are 88 area units in Hunan province. The most connected area unit has 11 neighbours. There are two are units with only one neighbour.
To view the content of the data table, you can either display the output data frame on RStudio data viewer or by printing out the first ten records by using the code chunk below.
nb_queenSimple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
First 10 features:
nb NAME_2 ID_3 NAME_3 ENGTYPE_3
1 2, 3, 4, 57, 85 Changde 21098 Anxiang County
2 1, 57, 58, 78, 85 Changde 21100 Hanshou County
3 1, 4, 5, 85 Changde 21101 Jinshi County City
4 1, 3, 5, 6 Changde 21102 Li County
5 3, 4, 6, 85 Changde 21103 Linli County
6 4, 5, 69, 75, 85 Changde 21104 Shimen County
7 67, 71, 74, 84 Changsha 21109 Liuyang County City
8 9, 46, 47, 56, 78, 80, 86 Changsha 21110 Ningxiang County
9 8, 66, 68, 78, 84, 86 Changsha 21111 Wangcheng County
10 16, 17, 19, 20, 22, 70, 72, 73 Chenzhou 21112 Anren County
County GDPPC geometry
1 Anxiang 23667 POLYGON ((112.0625 29.75523...
2 Hanshou 20981 POLYGON ((112.2288 29.11684...
3 Jinshi 34592 POLYGON ((111.8927 29.6013,...
4 Li 24473 POLYGON ((111.3731 29.94649...
5 Linli 25554 POLYGON ((111.6324 29.76288...
6 Shimen 27137 POLYGON ((110.8825 30.11675...
7 Liuyang 63118 POLYGON ((113.9905 28.5682,...
8 Ningxiang 62202 POLYGON ((112.7181 28.38299...
9 Wangcheng 70666 POLYGON ((112.7914 28.52688...
10 Anren 12761 POLYGON ((113.1757 26.82734...The print shows that polygon 1 has five neighbours. They are polygons number 2, 3, 4, 57,and 85.
One of the advantage of sfdep over spdep is that the output is an sf tibble data frame.
Identify contiguity neighbours: Rooks’ method
nb_rook <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry,
queen = FALSE),
.before = 1)Identifying higher order neighbors
There are times that we need to identify high order contiguity neighbours. To accomplish the task, st_nb_lag_cumul() should be used as shown in the code chunk below.
nb2_queen <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
nb2 = st_nb_lag_cumul(nb, 2),
.before = 1)Note that if the order is 2, the result contains both 1st and 2nd order neighbors as shown on the print below.
nb2_queenSimple feature collection with 88 features and 8 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
First 10 features:
nb
1 2, 3, 4, 57, 85
2 1, 57, 58, 78, 85
3 1, 4, 5, 85
4 1, 3, 5, 6
5 3, 4, 6, 85
6 4, 5, 69, 75, 85
7 67, 71, 74, 84
8 9, 46, 47, 56, 78, 80, 86
9 8, 66, 68, 78, 84, 86
10 16, 17, 19, 20, 22, 70, 72, 73
nb2
1 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 32, 56, 57, 58, 64, 69, 75, 76, 78, 85
2 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 32, 56, 57, 58, 64, 68, 69, 75, 76, 78, 85
3 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 32, 56, 57, 69, 75, 78, 85
4 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 57, 69, 75, 85
5 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 32, 56, 57, 69, 75, 78, 85
6 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 32, 53, 55, 56, 57, 69, 75, 78, 85
7 9, 19, 66, 67, 71, 73, 74, 76, 84, 86
8 2, 9, 19, 21, 31, 32, 34, 35, 36, 41, 45, 46, 47, 56, 58, 66, 68, 74, 78, 80, 84, 85, 86
9 2, 7, 8, 19, 21, 35, 46, 47, 56, 58, 66, 67, 68, 74, 76, 78, 80, 84, 85, 86
10 11, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 82, 83, 86
NAME_2 ID_3 NAME_3 ENGTYPE_3 County GDPPC
1 Changde 21098 Anxiang County Anxiang 23667
2 Changde 21100 Hanshou County Hanshou 20981
3 Changde 21101 Jinshi County City Jinshi 34592
4 Changde 21102 Li County Li 24473
5 Changde 21103 Linli County Linli 25554
6 Changde 21104 Shimen County Shimen 27137
7 Changsha 21109 Liuyang County City Liuyang 63118
8 Changsha 21110 Ningxiang County Ningxiang 62202
9 Changsha 21111 Wangcheng County Wangcheng 70666
10 Chenzhou 21112 Anren County Anren 12761
geometry
1 POLYGON ((112.0625 29.75523...
2 POLYGON ((112.2288 29.11684...
3 POLYGON ((111.8927 29.6013,...
4 POLYGON ((111.3731 29.94649...
5 POLYGON ((111.6324 29.76288...
6 POLYGON ((110.8825 30.11675...
7 POLYGON ((113.9905 28.5682,...
8 POLYGON ((112.7181 28.38299...
9 POLYGON ((112.7914 28.52688...
10 POLYGON ((113.1757 26.82734...Deriving contiguity weights: Queen’s method
Now, you are ready to compute the contiguity weights by using st_weights() of sfdep package.
Deriving contiguity weights: Queen’s method
In the code chunk below, queen method is used to derive the contiguity weights.
wm_q <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
wt = st_weights(nb,
style = "W"),
.before = 1) Notice that st_weights() provides tree arguments, they are:
nb: A neighbor list object as created by st_neighbors(). style: Default “W” for row standardized weights. This value can also be “B”, “C”, “U”, “minmax”, and “S”. B is the basic binary coding, W is row standardised (sums over all links to n), C is globally standardised (sums over all links to n), U is equal to C divided by the number of neighbours (sums over all links to unity), while S is the variance-stabilizing coding scheme proposed by Tiefelsdorf et al. 1999, p. 167-168 (sums over all links to n). allow_zero: If TRUE, assigns zero as lagged value to zone without neighbors.
wm_qSimple feature collection with 88 features and 8 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
First 10 features:
nb
1 2, 3, 4, 57, 85
2 1, 57, 58, 78, 85
3 1, 4, 5, 85
4 1, 3, 5, 6
5 3, 4, 6, 85
6 4, 5, 69, 75, 85
7 67, 71, 74, 84
8 9, 46, 47, 56, 78, 80, 86
9 8, 66, 68, 78, 84, 86
10 16, 17, 19, 20, 22, 70, 72, 73
wt
1 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2
2 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2
3 0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25
4 0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25
5 0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25
6 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2
7 0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25
8 0.1428571, 0.1428571, 0.1428571, 0.1428571, 0.1428571, 0.1428571, 0.1428571
9 0.1666667, 0.1666667, 0.1666667, 0.1666667, 0.1666667, 0.1666667
10 0.125, 0.125, 0.125, 0.125, 0.125, 0.125, 0.125, 0.125
NAME_2 ID_3 NAME_3 ENGTYPE_3 County GDPPC
1 Changde 21098 Anxiang County Anxiang 23667
2 Changde 21100 Hanshou County Hanshou 20981
3 Changde 21101 Jinshi County City Jinshi 34592
4 Changde 21102 Li County Li 24473
5 Changde 21103 Linli County Linli 25554
6 Changde 21104 Shimen County Shimen 27137
7 Changsha 21109 Liuyang County City Liuyang 63118
8 Changsha 21110 Ningxiang County Ningxiang 62202
9 Changsha 21111 Wangcheng County Wangcheng 70666
10 Chenzhou 21112 Anren County Anren 12761
geometry
1 POLYGON ((112.0625 29.75523...
2 POLYGON ((112.2288 29.11684...
3 POLYGON ((111.8927 29.6013,...
4 POLYGON ((111.3731 29.94649...
5 POLYGON ((111.6324 29.76288...
6 POLYGON ((110.8825 30.11675...
7 POLYGON ((113.9905 28.5682,...
8 POLYGON ((112.7181 28.38299...
9 POLYGON ((112.7914 28.52688...
10 POLYGON ((113.1757 26.82734...Distance-based Weights
There are three popularly used distance-based spatial weights, they are:
fixed distance weights, adaptive distance weights, and inverse distance weights (IDW).
Deriving fixed distance weights
Before we can derive the fixed distance weights, we need to determine the upper limit for distance band by using the steps below:
geo <- sf::st_geometry(hunan_GDPPC)
nb <- st_knn(geo, longlat = TRUE)! Polygon provided. Using point on surface.Warning in st_point_on_surface.sfc(geometry): st_point_on_surface may not give
correct results for longitude/latitude datadists <- unlist(st_nb_dists(geo, nb))! Polygon provided. Using point on surface.Warning in st_point_on_surface.sfc(geometry): st_point_on_surface may not give
correct results for longitude/latitude dataNow, we will go ahead to derive summary statistics of the nearest neighbour distances vector (i.e. dists) by usign the coced chunk below.
summary(dists) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
21.56 29.11 36.89 37.34 43.21 65.80 The summary statistics report above shows that the maximum nearest neighbour distance is 65.80km. By using a threshold value of 66km will ensure that each area will have at least one neighbour.
Now we will go ahead to compute the fixed distance weights by using the code chunk below.
wm_fd <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_dist_band(geometry,
upper = 66),
wt = st_weights(nb),
.before = 1)! Polygon provided. Using point on surface.Warning: There was 1 warning in `stopifnot()`.
ℹ In argument: `nb = st_dist_band(geometry, upper = 66)`.
Caused by warning in `st_point_on_surface.sfc()`:
! st_point_on_surface may not give correct results for longitude/latitude dataDeriving adaptive distance weights
In this section, you will derive an adaptive spatial weights by using the code chunk below.
wm_ad <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_knn(geometry,
k=8),
wt = st_weights(nb),
.before = 1)! Polygon provided. Using point on surface.Warning: There was 1 warning in `stopifnot()`.
ℹ In argument: `nb = st_knn(geometry, k = 8)`.
Caused by warning in `st_point_on_surface.sfc()`:
! st_point_on_surface may not give correct results for longitude/latitude dataCalculate inverse distance weights
In this section, you will derive an inverse distance weights by using the code chunk below.
wm_idw <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
wts = st_inverse_distance(nb, geometry,
scale = 1,
alpha = 1),
.before = 1)! Polygon provided. Using point on surface.Warning: There was 1 warning in `stopifnot()`.
ℹ In argument: `wts = st_inverse_distance(nb, geometry, scale = 1, alpha = 1)`.
Caused by warning in `st_point_on_surface.sfc()`:
! st_point_on_surface may not give correct results for longitude/latitude data